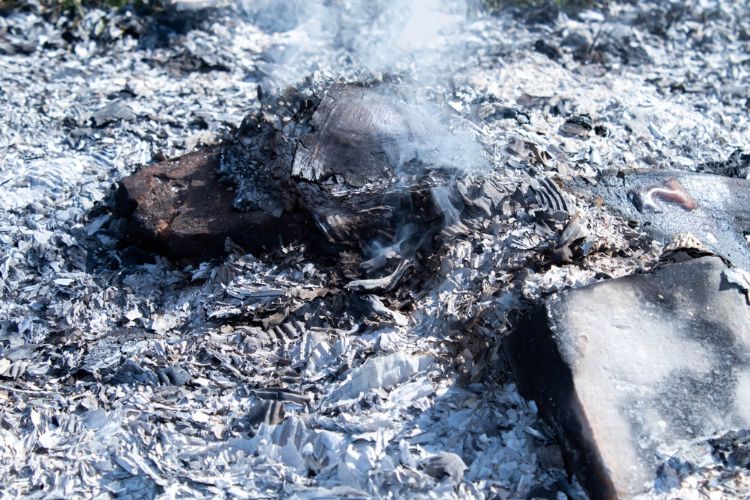
Have you ever stared down at the remains of a cosy fire or remnants from your barbecue and wondered, “What now?”
The grey, powdery substance left behind, commonly known as ash, isn’t just the end of a warm evening. It begins with a new question: How do you dispose of it safely?
But wait, before you go dusting it off into the garden or dumping it with your regular trash, there’s more to consider. You might be wondering, “Is it environmentally safe? Could there be health implications? What’s the most effective and hassle-free way to get rid of it?”
Enter the world of skip bins, your trusty sidekick in this ash disposal saga. Prepare to extinguish those burning questions you’ve been holding onto. Let’s dive in!
1. Introduction to Ash
Ash is the powdery residue that remains after the combustion of materials like wood, coal, or other organic substances.
It is primarily composed of fine particles that contain minerals, charred remnants, and sometimes trace metals. Often light grey to white in colour, ash can vary in its consistency, from very fine with a flour-like texture to coarser, gritty particles.
Originating from multiple sources like fireplaces, barbecues, industrial processes, and agricultural burns, ash is a common by-product found in many of our day-to-day activities.
While it may seem benign, handling and disposing of ash correctly is essential, especially considering its potential impacts on the environment and human health.
2. Types of ash
- Wood ash: Resulting from burning wood in fireplaces, stoves, and bonfires, it’s rich in potassium and lime and often repurposed for gardening.
- Coal ash: Produced from burning coal, commonly in power plants. It contains heavier metals, making it more hazardous.
- Cigarette ash: The residue from burned tobacco and paper in cigarettes.
- Volcanic ash: Fine particles of pulverised rock, minerals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions.
- Incinerator ash: Comes from the burning of municipal solid waste. It can be further classified into bottom ash and fly ash.
Handling each type requires specific precautions, especially when considering disposal via skip bins.
3. Health Hazards of Ash
- Respiratory issues: Inhalation of ash particles can irritate the lungs and aggravate existing respiratory conditions like asthma.
- Skin irritation: Direct contact may cause skin rashes or dryness.
- Eye irritation: Fine ash particles can cause redness and a gritty feeling in the eyes.
- Heavy metals: Coal ash can contain hazardous heavy metals such as arsenic, lead, and mercury, which pose serious health risks if ingested or inhaled.
- Contaminated water: Ash can leach into water sources, posing risks if consumed.
4. Proper Disposal of Ash
Proper disposal of ash ensures both environmental and personal safety. Options include:
- Landfill disposal: Ash, especially from coal, should be disposed of in designated landfills to prevent the leaching of harmful substances.
- Composting: Wood ash can be added to compost in moderate amounts, enriching the soil with minerals.
- Recycling: Some industries recycle ash for use in construction materials or soil amendments.
Always check local regulations before disposing of ash. Some councils may have specific disposal or recycling programs.
When considering ash disposal, the type of ash and its source play a critical role. Skip bins are often the safest and most efficient means of ensuring containment and compliance with disposal guidelines.
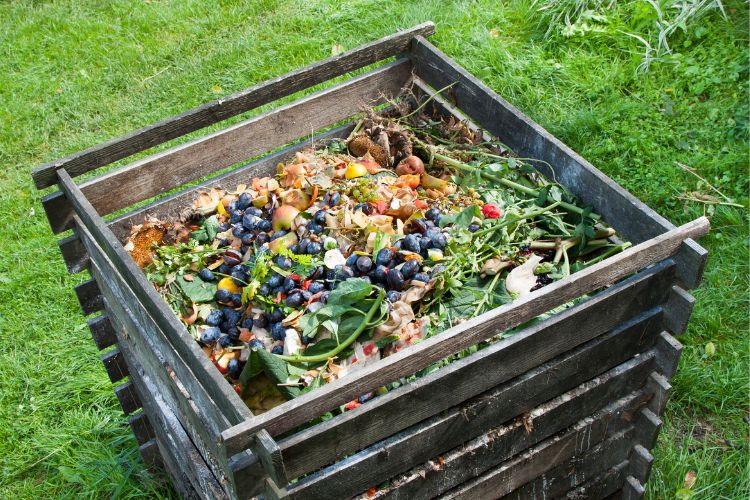

5. Benefits of Ash
While ash can pose challenges, it also offers several benefits:
- Soil enrichment: Wood ash is rich in minerals like potassium and lime, which can neutralise acidic soils and promote plant growth.
- Pest deterrent: When sprinkled in gardens, ash can deter pests like snails and slugs.
- Deicing agent: In colder regions, ash can be used as an eco-friendly alternative to salt for melting ice on pathways.
- Natural cleaner: Ash mixed with water forms lye, which has been traditionally used for cleaning and soap-making.
Remember, the benefits largely depend on the source of the ash, so always be sure about its origin before using it for anything.
6. Ash Disposal Regulations
The disposal of ash can vary based on regional regulations and the source of the ash. Here’s a general overview:
- Residential ash: Many councils advise residents to let ash cool for several days, then gently sprinkle it in gardens or place it in your green waste bin. To be safe, always check your local council’s guidelines.
- Business and commercial ash: Often requires a special disposal method, especially if produced in large volumes. Consult with waste management services in your area.
- Hazardous ash: Ash from certain materials or chemicals might be classified as hazardous waste. Such ash requires special handling and disposal.
- Local regulations: It is essential to consult your local council or waste disposal service for specific regulations related to ash disposal. They often provide guidance and resources tailored to your region’s needs.
Always prioritise safety and environmental considerations when dealing with ash disposal.
7. Skip Bins for Ash Disposal — Is there such a thing?
Skip bins are versatile containers ideal for a variety of waste disposal needs, including ash. However, is there a specific skip bin primarily for ash?
While most skip bin services might not have an “ash-only” bin, they certainly provide containers suitable for ash disposal. However, it’s essential that the ash is cold and free from live embers.
When inquiring about skip bin hire, mention your requirement to dispose of ash, and the team will guide you to the most suitable option. Always prioritise safety and consult with the experts for the best disposal recommendations.
8. Ash Disposal Alternatives
- Composting: Cold wood ash can be mixed with compost materials. The potassium and lime content can be beneficial for certain plants.
- Garden amendment: Used in moderation, ash can enrich garden soil, enhancing the growth of certain vegetables.
- Pest repellent: Sprinkling ash can deter pests like slugs and snails from gardens.
- Cleaning agent: Ash, especially from hardwood, can be used as a mild abrasive for cleaning metals.
- Landfills: If you have large quantities, some landfills accept ash. Always contact your local council to ensure proper procedures are followed.
- Recycling centres: Some centres accept ash for recycling into various products, like bricks or road-basing materials.
9. Ash Disposal Costs
- Skip bin hire: Depending on the size, hiring a skip bin specifically for ash disposal can range from $150 to $600.
- Landfill fees: Disposing of ash at a landfill typically incurs a weight-based fee. Expect to pay anywhere from $20 to $100 per tonne.
- Recycling centres: Some centres might charge a fee, ranging from $10 to $50, depending on the quantity.
- Collection services: Some waste management services offer ash collection, with prices starting at $50 and increasing based on volume and frequency.
- Garden and pest control usage: Using ash in gardens or as a pest deterrent is generally cost-effective, often requiring only transportation or small containment costs.
10. Environmental Impact of Ash Disposal
Ash disposal can have varied environmental impacts based on the method chosen. Here are your options:
- Landfills: Sending ash to landfills can contribute to landfill overflow and may leach harmful substances into the soil, potentially affecting waterways and the broader environment.
- Recycling: Certain types of ash, like wood ash, can be recycled into beneficial products, reducing its environmental footprint.
- Composting: Ash from organic materials can be added to compost in small amounts, benefiting the soil by returning essential minerals.
- Garden use: When used appropriately, ash can enrich garden soil, but it’s essential to ensure it doesn’t harm plants or adversely affect soil pH.
- Containment: Securely containing ash in specially designed bins or containers minimises its environmental impact, especially if it contains harmful chemicals or materials.
Navigating the Ash Landscape: Sustainability and Next Steps
The disposal of ash isn’t just a mere task but a responsibility towards our environment, city, and community. Our choices can impact sustainability, affecting life in numerous locations.
While events in our daily lives often produce waste, it’s essential to recognise the significance of proper disposal and the potential hazards of mishandling.
People play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable future. Our community needs to support sustainable projects and methods.
Best Price Skip Bins offers solutions tailored to your skip bin hire and ash disposal needs, ensuring environmental support and sustainability. Contact us today to get a quote and learn more about our services! Here at Best Price Skip Bins, we serve all major regions, including Melbourne, Sydney, Adelaide, Perth, Brisbane, the Sunshine Coast and the Gold Coast.